Science News
A New Age of Electron Microscopy: Magnifying Possibilities with Automation
Researchers at Berkeley Lab developed a method for automated microscopy, a streaming service for faster data transfer, and a web-based platform called Distiller that brings the two together. Read More »
DESI Opens Access to the Largest 3D Map of the Universe Yet
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is mapping millions of celestial objects to better understand dark energy; today, the DESI collaboration released a new collection of data for anyone in the world to investigate. Read More »
Simulation Confirms Method for More Efficient Fusion
With the help of supercomputers at NERSC, researchers at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have confirmed through simulations a method that stops the production of certain unused waves, improving the efficiency of the fusion reaction. Read More »
Durable New Catalyst Solves Persistent Chemistry Problem
With support from the Perlmutter supercomputer at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), scientists have tackled a long-standing problem in industrial chemistry. Read More »
AI Shows Promise for Mapping Disease Progression
With help from NERSC’s Perlmutter supercomputer, researchers have proposed a framework for investigating “embeddings,” representations of objects like text designed to be consumed by AI models such as large language models (LLMs). Read More »
Perlmutter Helps Identify 'Exquisite' Gravitational Lens
Using the Perlmutter supercomputer at NERSC, an abundance of new data from the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys, and recent observations from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles, Berkeley Lab, and collaborating institutions have identified a unique configuration of seven galaxies forming the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens ever discovered. Read More »
Magnifying Deep Space Through the 'Carousel Lens'
An unprecedented discovery by the DESI collaboration has generated a computational model with promise for measuring elusive cosmic parameters like dark matter and dark energy. Read More »
Collaboration Exploring Neutral Atom Technology Expanded for Second Year
NERSC has teamed up with the Boston-based quantum computing company QuEra Computing, exploring an up-and-coming approach to quantum computing known as neutral atom technology. After a successful first year punctuated with strong scientific results, the partnership has been extended. Read More »
Tropical Cyclones Intensifying Due to Warming Atmosphere
Using computational resources at NERSC, researchers from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Berkeley Lab, and partnering institutions have gained a better understanding of how tropical cyclones near coastal regions have intensified over time, the likely causes of the change, and what the future might hold according to climate models. Read More »
Gravitational Form Factors Illuminate Substructure of the Proton
Using simulations performed on NERSC’s Perlmutter system, a team of researchers used lattice quantum chromodynamics (lattice QCD) to understand for the first time certain aspects of how quarks and gluons form the structure of the proton. Read More »
QIS@Perlmutter Fuels Discoveries and Collaborations in Quantum Computing
Since its launch in 2022, NERSC's QIS@Perlmutter program supporting novel quantum information science (QIS) projects has exceeded expectations, generating strong engagement among researchers and fueling numerous discoveries in quantum computing. Read More »
New Alloy Won't Crack at Extreme Temperatures
With the help of NERSC systems, researchers have uncovered a metal alloy that won’t crack at extreme temperatures. The discovery could open the door to next-generation engines that can operate at higher efficiencies. Read More »
DIII-D National Fusion Facility, NERSC, AMCR, and ESnet Collaboration Speeds Nuclear Fusion Research
High performance computing at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), the Energy Sciences Network (ESnet)'s high-speed data network, and DIII-D's rich diagnostic suite combine to enable near-real-time analysis of massive quantities of data during experiments, allowing tailoring of the experimental process — and accelerating the pace of experimental science. Read More »
Hunting for 'Cracks' in the Standard Model
With the help of computing power from NERSC, researchers from the Majorana Collaboration – which includes more than 50 researchers from more than 20 institutions in four countries – used detectors at the Sanford Underground Research Facility (SURF) in Lead, South Dakota, to search for violations of quantum mechanics. Read More »
Perlmutter Supports CO2 Fixation for Carbon-Negative Building Materials
Locking greenhouse gases into building materials could store them safely for many years. Researchers using NERSC resources are advancing the science behind this idea. Read More »
Collaboration Fuels High-Speed, Data-Intensive Research to Understand How Nuclei Decay
A technical evaluation using data from a recent scientific-user experiment has demonstrated how ESnet enables FRIB scientists to send large amounts of data across the country, use NERSC's Perlmutter supercomputer to analyze it in near-real time, and return results, enabling quicker data-informed experimental choices. Read More »
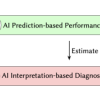
AI-based Approach Speeds Diagnosis of I/O Performance Bottlenecks in HPC
Using NERSC systems, researchers from Berkeley Lab have developed a novel AI-based method for diagnosing input/output (I/O) performance bottlenecks in high performance computing (HPC) that automatically identifies these bottlenecks at the job level and offers potential solutions. Read More »
Simulating Plasma, NERSC Systems Enable Efficient Microchip Production
Researchers at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory used supercomputers at NERSC to develop new simulation codes that improve current methods of producing microchips using plasma. Read More »
Perlmutter Provides Peek into Interior of Ice Giant Planets
Researchers at UC Berkeley used the Perlmutter supercomputer at NERSC to make progress toward a better understanding of chemistry inside ice giant planets, a step forward for planetary science that may also have applications on Earth. Read More »
NERSC Helps Uncover the Mechanism Behind the ‘Dolomite Problem’
Using supercomputers at NERSC, researchers have revealed the key mechanism that inhibits dolomite growth and explained how the mineral forms in nature. Read More »
Cori and Perlmutter Support New Understanding of Reaction Behind Salt-Based Nuclear Reactors
Using computing resources at NERSC, researchers have shown how electrons interact with ions of molten salts, providing insights into the processes that could occur inside next-generation salt-based nuclear reactors known as molten-salt reactors (MSRs). Read More »
NERSC Collaborations Help Illuminate Earth's Biodiversity
With the help of supercomputers at NERSC and support from the DOE's Exascale Computing Project, researchers in Berkeley Lab’s Applied Mathematics and Computational Research Division and at the Joint Genome Institute have developed new tools to advance the field of metagenomics and expand scientists’ understanding of our world’s biodiversity. Read More »
Perlmutter Supports First Gravitational Lensing System Modeled on GPUs
Using the GIGA-Lens modeling code on the Perlmutter supercomputer at NERSC, a team of researchers has modeled a rare instance of strong gravitational lensing known as an Einstein Cross—likely the first such system to be modeled on GPUs and a demonstration of the promise of GPU-accelerated modeling. Read More »
NERSC Assists in Search for More Sustainable EV Batteries
NERSC is helping a Berkeley Lab-led consortium of researchers speed the commercialization of a new family of batteries with more energy-dense cathodes that don’t require metals in short supply. Read More »
NERSC Helps Scientists Build Public Health Datasets from Location Services
Prompted by the COVID pandemic, scientists used NERSC resources to process location-based cell phone data and produce more detailed datasets that help them better estimate social contacts within public spaces. Read More »
How Scientists Are Accelerating Next-Gen Microelectronics
With the help of NERSC supercomputing resources and expertise, the newly launched Center for High Precision Patterning Science is developing a technique to pack over 100 billion transistors into a microchip the size of a fingernail. Read More »
NERSC Powers Insight Into Chemical Actuation of Self-Folding Origami Machines
3D microfabrication based on origami-inspired materials is a promising technique for building materials, structures, devices, and systems with unconventional electronic, mechanical, and optical properties. Read More »
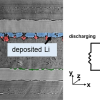
Using Deep Learning to Assess Lithium Metal Battery Performance
A team of researchers from Berkeley Lab’s Center for Advanced Mathematics for Energy Research Applications and colleagues have developed batteryNET, a deep learning algorithm that enhances the assessment of lithium agglomeration in solid-state lithium metal batteries. Read More »
Three New Studies Emerge from NERSC Research on Climate Change, Extreme Weather
NERSC is a hub for climate and weather research, and three recent scientific journal articles all published within one month highlight the center’s continuing role in supporting this work. Read More »
DESI Early Data Release Holds Nearly Two Million Objects
NERSC makes the first batch of data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument available for researchers to mine. Read More »
NERSC Supports First All-GPU Full-Scale Physics Simulation
Using supercomputers at NERSC, researchers have completed a simulation of a detector of neutrino interactions that’s designed to run exclusively on graphics processing units (GPUs)—the first simulation of its kind and an example of using GPUs’ highly parallel structure to process large amounts of physical data. Read More »
QIS Project Shows Novel Method for Privacy-Preserving Quantum ML
Scientific results from the initial QIS@Perlmutter projects are starting to emerge; in one recently published paper, a research group shared results of a quantum machine learning project that explores novel methods for preserving privacy within advanced quantum computing functions.
Read More »
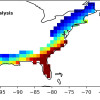
Computational Modeling Streamlines Hunt for Battery Electrolytes
Using computing resources at NERSC at Berkeley Lab, researchers from the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research have identified new, more efficient ways to find improved electrolytes for batteries. By computationally modeling molecules and virtually observing their properties, researchers can identify the most promising ones and save experimental scientists from spending time and resources on those that won’t work. Read More »
New Math Methods and Perlmutter HPC Combine to Deliver Record-Breaking ML Algorithm
Using the Perlmutter supercomputer at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have devised a new mathematical method for analyzing extremely large datasets – and, in the process, demonstrated proof of principle on a record-breaking dataset of more than five million points. Read More »
Shining a light on electrons’ role in energy transfer among 2D materials
Using the Cori supercomputer, a group of scientists examined heat and energy movements between certain 2D materials, spurring discoveries that could pave the way for a new generation of transistors Read More »
Berkeley Lab Works Toward a Connected Future for Science
Superfacility is a conceptual model of seamless connection between experimental facilities and high performance computing resources – an integrated and automated system for gathering, transporting, and analyzing scientific data in real time. Berkeley Lab is working to standardize, automate, and scale up the processes needed for superfacility onsite across the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), and beyond. Read More »
The Most Advanced Bay Area Earthquake Simulations Will be Publicly Available
A collaboration involving scientists and computing resources from Berkeley Lab and the simulation software EQSIM is releasing the most accurate and detailed earthquake simulations to date, which will initially capture earthquake motions across the San Francisco Bay Area and later expand to other regions. Read More »
WarpX Code Shines at the Exascale Level
The WarpX project has spent the last six years creating a novel, highly parallel, and highly optimized single-source simulation code for modeling plasma-based particle colliders on cutting-edge exascale supercomputers, with broad importance for other accelerators and related problems. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Scientists Create Machine Learning Pipeline for Interpreting Large Tomography Datasets
A group of Berkeley Lab scientists has developed and tested several machine learning techniques organized in a learning pipeline to improve the interpretation of increasingly large cryo-ET datasets. Read More »
Perlmutter Results Show Progress in Quantum Information Science
The QIS@Perlmutter initiative at NERSC aims to support research in the space of quantum information science (QIS) conducted on the Perlmutter supercomputer, including quantum simulation of materials and chemical systems, algorithms for compilation of quantum circuits, error mitigation for quantum computing, and development of hybrid quantum/classical algorithms. The first phase of the project will come to an end this month, but has begun to bear fruit in the form of early science results and collaborations across the field. Read More »
New Search Method Expands Horizon in Hunt for New Polymer Electrolytes
Using computing resources at NERSC, researchers at MIT, in partnership with the Toyota Research Institute, have pioneered a new method for using machine learning to screen for new materials, yielding the largest dataset of polymer electrolytes ever seen in the field and signaling progress for the search for new materials generally. Read More »
New Climate Models Reveal Geographical Link Between Wildfires and Extreme Weather
A climate study led by PNNL researchers used NERSC resources to investigate a growing connection between wildfires in the Western U.S. and extreme weather in the Central U.S. The team ran a series of models on Cori and detected an evolving relationship between wildfires in one region and frequencies of heavy rainfall and large hail in the other. Read More »
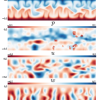
NERSC’s Cori System Helps Shed New Light on Plasma Turbulence
With the help of supercomputers at NERSC, Columbia University, and NASA, astrophysicists ran large-scale simulations that show the precise movements of electrons and ions in the sun’s plasma. Read More »
NERSC Summer Student Puts MPI Under the Microscope
This summer, as part of the Berkeley Lab Computing Sciences Summer Program, Muna Tageldin developed a microbenchmark to analyze variances in message-passing interface (MPI) performance on NERSC systems and look for the best statistical methods to characterize the results. Read More »
HPSS: Celebrating 30 Years of Long-term Storage for Scientific Research
This year marks the 30th anniversary of the HPSS Collaboration, a partnership between five DOE national laboratories and IBM. Today the High Performance Storage System is still going strong, serving some 40 sites around the world and more than 4 exabytes of production archival storage data. Read More »
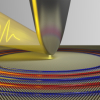
Materials Science Simulation Achieves Extreme Performance at NERSC
Powered by the new Perlmutter system at NERSC at Berkeley Lab, a team of researchers led by Paderborn University scientists Thomas D. Kühne and Christian Plessl used a new mixed-precision method to conduct the first electronic structure simulation that executed more than quintillion operations per second. Read More »
LUX-ZEPLIN Data-Management Needs Fuel Team Approach
The National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) and the Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) located at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) are playing a critical role in facilitating the burgeoning LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment in its search for dark matter in the universe.Located deep in the Black Hills of South Dakota in the Sanford Underground Research Facility (SURF), the uniquely sensitive LZ dark matter detector recently passed a check-out phase of startup… Read More »
NERSC Summer Student Works Toward Machine Learning for a Rainy Day
As part of the 2022 Berkeley Lab Summer Student program, UC Berkeley PhD student James Duncan works to improve the resolution of precipitation models using machine learning, aiming to produce more accurate weather prediction. Read More »
NERSC Simulations Target ‘Forever Chemicals’ in Soils
With the growing awareness about the risks posed by “forever chemicals” in our water, soil, plants, and more, researchers are making new inroads into understanding how these substances function and how we might be able to mitigate their harmful effects. Fortunately, supercomputer simulations are aiding in these efforts. Read More »
Neuroscience Simulations at NERSC Shed Light on Origins of Human Brain Recordings
Using simulations run at NERSC, a team of researchers at Berkeley Lab has found the origin of cortical surface electrical signals in the brain and discovered why the signals originate where they do. Read More »
Simulations at NERSC Drive Progress Toward Nuclear Fusion
Simulations performed at NERSC at Berkeley Lab have brought researchers one step closer to producing efficient, endlessly renewable energy through nuclear fusion, harnessing the process that produces light and heat in our Sun and other stars. Read More »
Machine Learning Fuels Materials Science and Search in Continuous Action Spaces
Using computing resources at NERSC at Berkeley Lab, researchers at Argonne National Laboratory have succeeded in exploring important materials-science questions and demonstrated progress using machine learning to solve difficult search problems. Read More »
Researchers Narrow Down Mass of Sought-After Axion Particle
Researchers at Berkeley Lab and other institutions have narrowed the range of possible masses for the axion, a theoretical particle that may make up much of the dark matter in the universe. Read More »
San Francisco and Berkeley Lab Team Up on Pioneering Climate Study
Berkeley Lab computational resources are helping the City and County of San Francisco adapt to the Bay Area's changing climate and the extreme storms it is expected to bring. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Helps Fuel Advances for Renewable Energy Sources
Simulations run at NERSC could enhance the development of a new artificial photosynthesis device component – a promising step forward in validating the viability of renewable fuels. Read More »
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: An Environmentally Friendly Transportation Alternative
In the quest to develop alternatives to fossil fuels for a variety of transportation methods, environmentally friendly hydrogen fuel cells are finding favor – and funding. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Computing Resources Enable Deeper Understanding of Supernovae Explosions
An international research team recently made history by recording the earliest post-explosion detection of a Type Ia supernova, using cosmological models developed at Berkeley Lab and supercomputing resources at NERSC. Read More »
X-Ray Crystallography Goes Even Tinier
Supported by high-performance computing resources at NERSC, scientists at Berkeley Lab have debuted a new form of X-ray crystallography for small molecules not previously conducive to investigation with crystallography. Read More »
Fire and Ice: How Arctic Sea Ice Influences Western U.S. Wildfires
New research from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory describes how climate conditions in one part of the world can, over time, influence climate outcomes thousands of kilometers away. Simulations run on Cori helped confirm this link Read More »
Perlmutter-Powered Deep-Learning Model Speeds Extreme Weather Predictions
Researchers from Berkeley Lab, Caltech, and NVIDIA trained the Fourier Neural Operator deep learning model to emulate atmospheric dynamics and provide high-fidelity extreme weather predictions across the globe a full five days in advance. Read More »
NERSC Targets Exascale with Perlmutter and the Exascale Science Applications Program
With an eye toward the first generation of exascale computing, in 2021 NERSC unveiled its newest supercomputer, Perlmutter. To ensure that users can readily utilize this next-generation technology, NERSC has been working with development teams to prepare codes for Perlmutter and the coming exascale systems through NESAP. Read More »
NERSC Resources Power Advances in Solar Cell Efficiency
The steady improvement in silicon-based solar cells has made them cost competitive with fossil fuel sources, and additional advances in their efficiency will make them even more attractive. New materials such as hybrid perovskites are poised to give solar-cell efficiency a boost, and research being conducted at NERSC is helping to pick up the pace. Read More »
Project Jupyter: A Computer Code that Transformed Science
As Project Jupyter becomes an increasingly important tool for data science, HPC sites around the world are responding to the demand by looking for ways to effectively support them. And NERSC has been at the forefront of this effort. Read More »
Study of Harvey Flooding Aids in Quantifying Climate Change
How much do the effects of climate change contribute to extreme weather events? A new study investigated the question for one particular element of one significant storm: Hurricane Harvey. Read More »
Limit global warming to 1.5°C and halve the land ice contribution to sea level this century
A new study predicts that sea-level rise could be halved this century (from today to 2100) if we meet the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to 1.5°C. This work combines nearly 900 simulations, including some of Berkeley Lab Computational Scientist Dan Martin's BISICLES models of Antarctic ice sheets. Read More »
NERSC and ESnet Take Scientific Data Collaboration to the Next Level
When the Dark Energy Science Collaboration needed a fast, secure, and convenient way to share large data sets with scientists outside of the collaboration, they turned to Berkeley Lab Computing Sciences for help, ultimately choosing an innovative data-sharing solution: the Modern Research Data Portal. Read More »
Designing Selective Membranes for Batteries Using a Drug Discovery Toolbox
Researchers have designed a polymer membrane with molecular cages built into its pores that could allow high-voltage battery cells to operate at higher power and more efficiently, important factors for both electric vehicles and aircraft. Read More »
NERSC Aids PPPL in Plasma Rocket Breakthrough
A revolutionary new rocket engine design has come out of Princeton University, with an assist from the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Read More »
How Urbanization and Pollution Increase Storm Activity Around Cities
Using NERSC’s Cori system, PNNL researchers modeled the effects of urban land and aerosols on storm patterns in two major U.S. cities. Read More »
HPC Explorations of Supernova Explosions Help Physicists Reach New Milestones
For more than 60 years, physicists have been studying the question of how supernova explosions occur. Thanks to the increasing power of supercomputing resources such as those at NERSC, they’re moving ever closer to an answer. Read More »
Superfacility Model Brings COVID Research Into Real Time
Researchers at NERSC and the Linac Coherent Light Source at SLAC are collaborating to leverage the superfacility model for real-time data analysis in the worldwide quest to decipher the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Read More »
Novel Data Processing Technique Aids XFEL Protein Structure Analysis
Scientists use X-ray crystallography to determine the three-dimensional structures of proteins. A new data processing approach is enhancing the outcomes. Read More »
Measurements of Pulsar Accelerations Reveal Milky Way’s Dark Side
It is well known that the expansion of the universe is accelerating due to a mysterious dark energy. Within galaxies, stars also experience an acceleration, though this is due to some combination of dark matter and stellar density. Researchers using NERSC supercomputers have obtained the first direct measurement of the average acceleration taking place within our home galaxy, the Milky Way. Read More »
Novel Calculation Sheds New Light on Matter/Anti-Matter Mystery
An international collaboration of theoretical physicists has published a novel calculation that provides new insights into the relationship between matter and antimatter in the universe. This work included extensive use of NERSC supercomputing resources over six years. Read More »
Deep-Learning Research Nominated for Best Student Paper Award at SC20
A paper describing MeshfreeFlowNet — an open-source, physics-constrained, deep-learning approach for simultaneously enhancing the spatial and temporal resolution of scientific data — is a finalist for the Best Student Paper Award at SC20.“MeshfreeFlowNet is a big step forward in terms of physics-constrained machine learning algorithm development, combining important criteria necessary for scientific data: physics-based partial differential equation constraints, a mesh-free design that… Read More »
NERSC Supports COVID-19 Pandemic Response
Since April 2020, NERSC has allotted 2.5 million node hours on its Cori supercomputer and has provided dedicated HPC staff liaisons and other resources to support COVID-19 research. Read More »
Physical Scientists Turn to Deep Learning to Improve Earth Systems Modeling
The role of deep learning in science is at a turning point, with weather, climate, and Earth systems modeling emerging as an exciting application area for physics-informed deep learning. In this Q&A, NERSC's Karthik Kashinath discusses what is driving the scientific community to embrace these new methodologies. Read More »
NERSC Resources Play Key Role in CUPID-Mo Collaboration
Nuclear physicists affiliated with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) played a leading role in analyzing data for a demonstration experiment that has achieved record precision for a specialized detector material. The data-analysis component of this ground-breaking research was conducted entirely at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), a DOE Office of Science user facility located at Berkeley Lab. Read More »
Spectacular ultraviolet flash may finally explain how white dwarfs explode
For just the second time ever, astrophysicists have spotted a spectacular flash of ultraviolet light in a supernova, an extremely rare event following a white dwarf explosion. Read More »
Supercomputing Pipeline Aids DESI’s Quest to Create 3D Map of the Universe
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument is combining high-speed automation, high-performance computing, and high-speed networking to produce the largest 3D map of the universe ever created. Starting in late 2020, DESI's five-year mission is to capture light from 35 million galaxies and 2.4 million quasars and transmit that data to NERSC - DESI’s primary computing center - for data processing and analysis. Read More »
Making Quantum ‘Waves’ in Ultrathin Materials
Running calculations at NERSC, a team of researchers co-led by Berkeley Lab have revealed how wavelike plasmons could power up a new class of sensing and photochemical technologies at the nanoscale. Read More »
Machine Learning Could Provide Unexpected Scientific Insights into COVID-19
A new text-mining tool developed at Berkeley Lab and supported by NERSC supercomputing resources is using natural language processing techniques that could yield unexpected scientific insights into COVID-19. Read More »
World's First 3D Simulations of Superluminous Supernovae
For the first time ever, an international team of astrophysicists simulated the 3D physics of superluminous supernovae—which are about a hundred times more luminous than typical supernovae—with NERSC supercomputers and the CASTRO code. Read More »
Harnessing the Power of Exascale for Wind Turbine Simulations
ExaWind, a DOE Exascale Computing Project, is developing new simulation capabilities to more accurately predict the complex flow physics of wind farms, and Berkeley Lab is bringing its adaptive mesh refinement expertise to the project to help make this happen. Read More »
NERSC’s Scientific Computing Power Steps into Coronavirus Battle
Researchers from the City of Hope’s Beckman Research Institute and the Translational Genomics Research Institute will use NERSC computing resources to help battle the COVID-19 global pandemic. Read More »
Earlier Spring Foliage Brings Warmer Air to the North
A group of researchers used NERSC to explore how early leaf growth, or “leaf-out,” affects the earth’s ecosystem. Their findings show that early spring leaf-out is causing a definitive increase in annual surface warming in the Northern Hemisphere. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Collaborates to Prepare Photovoltaic Materials Research for Exascale
NERSC and CRD researchers are part of a collaboration that is using BerkeleyGW software to enhance the search for new, more efficient photovoltaic solar cell materials on the first exascale computers. Read More »
NOAA Releases Extended Version of 20th Century Reanalysis Project
Calling it a time machine for weather data and a treasure trove for climate researchers, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has released an updated version of the 20th Century Reanalysis Project (20CRv3) - a high-resolution, four-dimensional reconstruction of the global climate that estimates what the weather was every day back to 1806. The release of this latest 20CRv3 data comes on the heels of an October 2019 release of data going back to 1836. Together, these new… Read More »
Deep Learning Expands Study of Nuclear Waste Remediation
A research collaboration between Berkeley Lab, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Brown University, and NVIDIA has achieved exaflop performance with a deep learning application used to model subsurface flow in the study of nuclear waste remediation. Read More »
NERSC Powers Research on Post-Wildfire Water Availability
Scientists at Berkeley Lab recently took a closer look at how wildfires affect California’s watersheds. Computer simulations run at NERSC allowed them to identify the regions in the watershed that were most sensitive to wildfire conditions, as well as the hydrologic processes that are most affected. Read More »
NERSC Resources Help PPPL Team Predict Plasma Pressure in Future Fusion Facilities
Researchers at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory have developed new insights into the physics governing the balance of pressure in the scrape-off layer, the thin strip of gas at the edge of the plasma in a tokamak reactor. Read More »
Hydrogen a Culprit in Capacity Loss of Sodium-Ion Batteries
Using NERSC's Cori system, UC Santa Barbara computational materials scientist Chris Van de Walle and colleagues have uncovered a reason for the loss of capacity that occurs over time in sodium batteries. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Deep Learning Expertise Draws Attention at International Climatology Meeting
Berkeley Lab’s growing expertise in applying machine learning methods to extreme weather event studies led to invitations to present at the 2019 International Meeting on Statistical Climatology, a prestigious event held only every three years. Read More »
Scientists Piece Together the Largest U.S.-Based Dark Matter Experiment
Most of the remaining components needed to fully assemble an underground dark matter-search experiment called LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) arrived at the project’s South Dakota home during a rush of deliveries in June. Once it is up and running, data captured by the detectors’ electronics will ultimately be transferred to NERSC, LZ’s primary data center, via ESnet. Read More »
Three Sky Surveys Completed in Preparation for Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument
It took three sky surveys – conducted at telescopes in two continents, covering one-third of the visible sky, and requiring almost 1,000 observing nights – to prepare for a new project that will create the largest 3D map of the universe’s galaxies and glean new insights about the universe’s accelerating expansion. Read More »
NERSC’s Cori System Reveals Integral Role of Gluons in Proton Pressure Distribution
For the first time, lattice quantum chromodynamics calculations run at NERSC allowed nuclear physicists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to determine the pressure distribution inside a proton, taking into account the contributions of the proton’s fundamental particles: quarks and gluons. Read More »
Cleaning Cosmic Microwave Background Data to Measure Gravitational Lensing
Gravity from distant galaxies cause tiny distortions in cosmic microwave background temperature maps - a process called gravitational lensing - which are detected by data analysis software run on supercomputers like the Cori system at NERSC. Unfortunately, this temperature data is often corrupted by foreground emissions from extragalactic dust, gas, and other noise sources that are challenging to model. So Berkeley Lab researchers developed a statistical method for analyzing CMB data that is largely immune to the foreground noise effects.
Read More »
CosmoGAN: Training a Neural Network to Study Dark Matter
A Berkeley Lab-led research group is using a deep learning method known as generative adversarial networks to enhance the use of gravitational lensing in the study of dark matter. Read More »
Superfacility Framework Advances Photosynthesis Research
Researchers have long studied PSII, a protein complex in green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria that plays a crucial role in photosynthesis. Their understanding of this three-billion-year-old biological system is now moving more quickly, thanks to an integrated superfacility framework established between LCLS, ESnet, and NERSC. Read More »
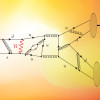
A Breakthrough in the Study of Laser/Plasma Interactions
A new 3D particle-in-cell simulation tool developed by researchers from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and CEA Saclay is enabling cutting-edge simulations of laser/plasma coupling mechanisms that were previously out of reach of standard PIC codes used in plasma research. Read More »