Science Vignettes
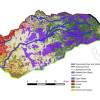
How California Wildfires Can Impact Water Availability
Berkeley Lab researchers used NERSC supercomputers to show that conditions left behind by California wildfires lead to greater winter snowpack, greater summer water runoff and increased groundwater storage. Read More »
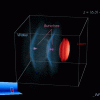
Petawatt Laser Guiding and Electron Beam Acceleration to 8 GeV in a Laser-Heated Capillary Discharge Waveguide
Researchers at Berkeley Lab’s BELLA Center set a new world record in laser-driven plasma-based electron acceleration by obtaining beams with an energy of up to 7.8 GeV in a 20 cm-long plasma using the high-power BELLA laser. The maximum achieved energy nearly doubled their previous record set in 2014. Read More »
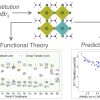
Machine-Learned Impurity Level Prediction in Semiconductors
Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) researchers ran high-throughout atomistic simulations on NERSC supercomputers and generated comprehensive computational datasets of impurity properties in two classes of semiconductors: lead-based hybrid perovskites and Cd-based chalcogenides. These datasets led to machine learned models which enable accelerated prediction and design for the entire chemical space of materials and impurities in these semiconductor class. Read More »
Magnetic Reconnection: A bridge to Plasma Kinetic Scales
Researchers from Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) used Cori to show that magnetic reconnection in a collisional plasma current sheet generates electric forces that overcome the collisional friction, leading to the spontaneous formation of current sheets and magnetic flux-ropes at the kinetic micro-scales.
Read More »
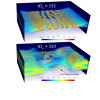
DOE Models Simulate Antarctic Ice Sheet Evolution
Ice sheet models developed under a DOE SciDAC project and run at NERSC have contributed to three international model intercomparison projects focused on assessing the future evolution of the Antarctic ice sheet. Read More »