COVID-19 HPC Consortium
The COVID-19 High Performance Computing Consortium is a unique private-public effort brings together federal government, industry, and academic leaders to volunteer free computing time and resources on their world-class machines. Scientists are invited to submit COVID-19 related research proposals. An expert panel of top scientists and computing researchers will select projects based on public health benefits, with an emphasis on rapid results. Proposals are reviewed and awards matched to resources with a very fast turnaround.
Structure Refinement of the Spike Protein of SARS-COV-2
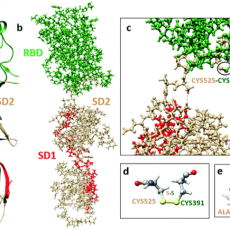
University of Missouri, Kansas City scientists are refining the structure of regions on the SARS-COV-2 to much higher accuracy using large scale ab initio simulations and investigating their atomic scale interactions and intra molecular binding mechanisms. Read More »
Dependence of Structure and Dynamics of Novel SARS-CoV-2 on Temperature and Humidity in the Atmosphere
Researchers from National Institute of Technology Warangal are studying whether the virus undergoes any biophysical changes in response to changes in atmospheric conditions, mainly temperature and humidity. Read More »
Drug-Repurposing for Covid-19 with 3D-Aware Machine Learning
Scientists from MIT and Harvard are exploring whether the repurposing of drugs for COVID-19 treatment can be accelerated with a combination of physical simulation and machine learning (ML). Read More »
Structure Refinement of the Spike Protein of SARS-COV-2
University of Missouri, Kansas City scientists are refining the structure of regions on the SARS-COV-2 to much higher accuracy using large scale ab initio simulations and investigating their atomic scale interactions and intra molecular binding mechanisms. Read More »
Dependence of Structure and Dynamics of Novel SARS-CoV-2 on Temperature and Humidity in the Atmosphere
Researchers from National Institute of Technology Warangal are studying whether the virus undergoes any biophysical changes in response to changes in atmospheric conditions, mainly temperature and humidity. Read More »
Manipulation of Membrane Curvature by Designer Peptides for Battling COVID-19 Infection
Scientists from Boston University and UCLA are working closely to understand the factors (sequence and membrane composition) that dictate the activity of SARS-CoV-2 "inverse translocation peptides" and their effect on the structure of the human cell membranes . Read More »
The Competition of Antiviral Drugs with ATP to Inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase: A Key to Enhanced Drug Screening
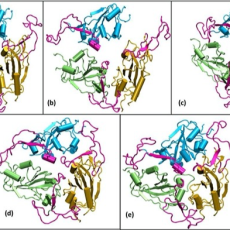
Researchers from the University of Alberta, Natural Resources Canada, and the National Research Council Canada and usage a novel computational approach for the enhanced screening of drugs, considering their effects in solution with ATP. The project addresses the question of why molecular dynamics studies of some drugs’ behavior in isolation show strong interference with viral replication, but clinical trials show lower impacts than might be expected. Read More »
Simulations of Mutated Indinavir and Hydroxychloroquine-SARS-CoV-2 Protease Complexes
The stability of the mutant Hydroxychloroquine-protease complexes over the time period of 50-100 nanoseconds will determine whether the drug is responsive towards a mutating SARS-CoV-2. The research is being conducted by scientists at the Shri Ramaswami Memorial University of Science and Technology. Read More »
Modeling and Simulation of Urban Transportation Systems for Return to Operations
Using Berkeley Lab's agent-based transportation demand model, BEAM (Behavior, Energy, Autonomy, Mobility), this project is analyzing a set of scenarios of future travel demand and transit service. Read More »